Education Links
Leaving Cert
 Maths
Maths
 French
French
 English
English
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Physics
Physics
 Biology
Biology
 Economics
Economics
 Spanish
Spanish
 Geography
Geography
 History
History
Junior Cert
A sequence is written as:
Notes
(i) A sequence which goes on forever is called an infinite sequence.
A sequence which stops is called a finite sequence.
(ii)
Example 1
In the sequence(iii) The General term
If you know the general term of a sequence you can work out any other term.
Example 2
If the general term of a sequence is given byFind
Solution
(iv)
Example 3
IfSolution
(a) The Sum of the first n terms
Students often get un and
Example 4
For the sequence:Solution
(b) Relationship between
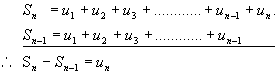
Notes: (i) This is a very important result as it is true for all sequences.
(ii) Given
(iii) In a later article we will see how to get
Example 5
IfSolution
Example 6
IfShow that
Solution
Example 7
IfSolution
Example 8
IfSolution


