Education Links
Leaving Cert
 Maths
Maths
 French
French
 English
English
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Physics
Physics
 Biology
Biology
 Economics
Economics
 Spanish
Spanish
 Geography
Geography
 History
History
Junior Cert
1. Modulus Equations
2. Exponential Equations
3. Log Equations
4. Surd Equations
1. Modulus Equations
The modulus of a real number is its distance to the origin on the number line. The notation is 2 vertical bars.
Notation: |Number| = The distance of the number from the origin.
Therefore |5| = 5 and |-6| = 6.
If you are asked to solve |x| = 7, this means you must find number(s) x which are 7 units from the origin. The solution is of course x = 7 and x = -7. This example gives the clue to solving more difficult problems.
Trick: To solve a modulus equation remove the bars and put
Steps:
(i) Remove the bars and put
(ii) Solve both options.
(iii) If there are surds involved square both sides first.
(iv) Check your answers.
Example 1
Solve |x + 4| = 3x - 8Solution
Example 2
Solve |x - 3| = |2x - 7|
SolutionExample 3
Solve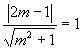
Solution
2. Exponential equations
These equations involve finding an unknown power.
Ex. If
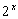 = 7 find x.
= 7 find x.Steps
(a) For products and quotients of exponential functions:
(i) Get all of the exponential functions on one side and the constants on the other side.
(ii) Simplify both sides.
(iii) If both sides can be expressed in the same base then equate the powers and solve the resulting equation.
(iv) If both sides cannot be expressed in the same base then take the log of both sides.
(b) For sums of exponential functions
(i) Isolate the common exponential function in each term and put it in a bracket. Call the object in the bracket u.
(ii) Rewrite the original equation in terms of u.
(iii) Solve for u and hence for the original variable.
Example 4
SolveSolution
Example 5
Solve ![]()
Solution
Example 6
SolveSolution
Example 7
SolveSolution
3. Log Equations
The trick for solving log equations is the technique which we call 'hooshing' (getting out of logs). The idea is based on a simple observation:
Trick (Hooshing): To get out of a log, hoosh the object on the other side up in the air, move the base of the log under it and rub out the log.
In general
Steps
(i) Get the same base.
(ii) Get all the logs on one side.
(iii) Get a single log.
(iv) Get out of logs (hoosh).
(v) Solve the resulting equation.
(vi) Check your answers.
Note: There are 2 ways to get the same base.
(a) Dropper:
(b) COB (Change of Base):
Example 8
SolveSolution
Example 9
SolveSolution
Example 10
SolveSolution
Example 11
SolveSolution
4. Surd Equations
These are equations involving square roots.
Steps:
(i) If there is only one surd isolate it on one side.
(ii) If there are 2 surds move one to the other side.
(iii) If there are 3 surds make sure one of them is on one side.
(iv) Square both sides and isolate any remaining surds.
(v) Square again to get rid of any remaining surds.
(vi) Solve the resulting equation.
(vii) Check your answers.
Example 12
SolveSolution
Example 13
SolveSolution
Example 14
SolveSolution


