Education Links
Leaving Cert
 Maths
Maths
 French
French
 English
English
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Physics
Physics
 Biology
Biology
 Economics
Economics
 Spanish
Spanish
 Geography
Geography
 History
History
Junior Cert
For the Leaving Cert. you must know 6 things about this equation.
(a) How to solve it: 2 methods (i) Factorization - quick but doesn't always work(ii) The Magic:
Notes:
- There are 2 solutions (roots) here.
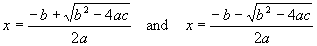
Because they are such a mouthful one is called a and the other b. - It always works
Remember as:
Remember as:
If the roots are a and b the equation is
Remember it as:
(d) The roots satisfy their own equation
If you are told that something is a root of
(e) The Discriminant
In the Magic the expression under the square root
If
If
Therefore if
If
(f) Graphs of Quadratics
The graphs of all quadratics are either Concave up (CUP) or Concave down (CAP)
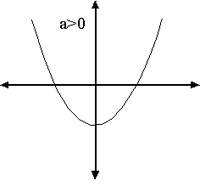
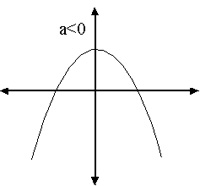
The roots a and b are the places where the curve crosses the x-axis.
A number of different types of problems involving the quadratic are now examined.
Type 1: Functions of a and b
Example 1
If a and b are the roots of(i) a + b (ii) ab (iii)
Solution
Type 2: Relationship between roots
Given a relationship between roots a and b you can be asked to find a relationship between the co-efficients a, b, c.
Let us consider some possibilities:
(i) one root is double the other: a, 2a
(ii) the roots add to 6: a, 6 - a
(iii) the sum of the roots is zero: a, -a
(iv) the roots are equal: a, a or b2 = 4ac (better)
(v) the product of the roots is 3: a,
(vi) one root is the reciprocal of the other: a,
(vii) the roots are in the ratio 3:4: 3a, 4a
Example 2
If one root ofSolution
Example 3
If the roots ofSolution
Type 3: New for Old/Two Quadratics
Example 4
If a and b are the roots ofSolution
Example 5
If a and b are the roots ofSolution


