Education Links
Leaving Cert
 Maths
Maths
 French
French
 English
English
 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Physics
Physics
 Biology
Biology
 Economics
Economics
 Spanish
Spanish
 Geography
Geography
 History
History
Junior Cert
Notation: ![]()
Think of a function which, when you differentiate it with respect to x, you get f(x).
Note: f(x) is called the integrand.
2. Rules of differentiation
(i) Sum Rule:
![]()
You can integrate each function of a sum of functions separately.
(ii) Multiplication by a constant rule:
![]()
You can take constants outside integrals.
3. Technique:
The most important technique on the core course is substitution. It is used for products and quotients of functions which cannot be simplified into a sum of simple functions.
Let u = that part of the integrand such that when you differentiate it you get a multiple of another part of the integrand.
4. Types of Integrals of the LC Course:
[A] Alint: Integrals with pure algebraic functions.
[B] Expint: Integrals with any hint of the exponential function.
[C] Logint: The inverse linear function.
[D] Trigint: Integrals with pure trig functions.
[E] Specials: Three algebraic functions that require unusual substitutions.
[A] Alint
The basis of Alint is
except when p = -1 when
In words: Add one to the power and divide by the new power for all powers except -1 when the answer is ln x.
Note 1:
Note 2:
Types of ALINT:
Type 1 - Straights: Sums of multiples of
Steps
Example 1
Evaluate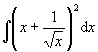
Solution
Example 2
EvaluateSolution
Type 2 - Products and quotients of Algebraic functions which cannot be simplified into sums of multiples of
Steps
Example 3
EvaluateSolution
Example 4
EvaluateSolution
Example 5
EvaluateSolution
Example 6
EvaluateSolution
[B] Expint
The basis of Expint is
Types of EXPINT:
Type 1 - Straights: Expofunctions which can be simplified into sums of expofunctions of the form
Steps
Example 7
EvaluateSolution
Example 8
EvaluateSolution
Type 2 - Products and Quotients of Expo and non-expo functions.
Steps
Example 9
EvaluateSolution
Example 10
EvaluateSolution
Type 3 - Products and quotients of pure expofunctions which cannot be simplified into a sum of expofunctions of the form
Steps
Example 11
EvaluateSolution
Example 12
EvaluateSolution
[C] Logint
This is the integration of the inverse linear function. It is based on
However, this can be extended to
Example 13
EvaluateSolution


